Chapter 8. Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
8.1. Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
8.2. Objective
8.3. Failure Modes & Their Probability
8.4. Required Documentation
8.5. Other Documentation
8.6. Data Sheets
8.7. FMEA Data Sheet
8.8. Advantages
8.9. Disadvantages
8.1. Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
FMEA is a qualitative inductive method that examines the failure of individual components to understand their effect on the system. Emphasis is placed on hardware failure. This analysis also requires an experienced team to conduct the analysis.
8.2. Objective
To organize and document what is known about the effect of component failures on a specified system
The objective of FMEA is to organize and document what is known about the effect of component failures on a specified system. In doing this you must define the complete functional boundaries of a system.
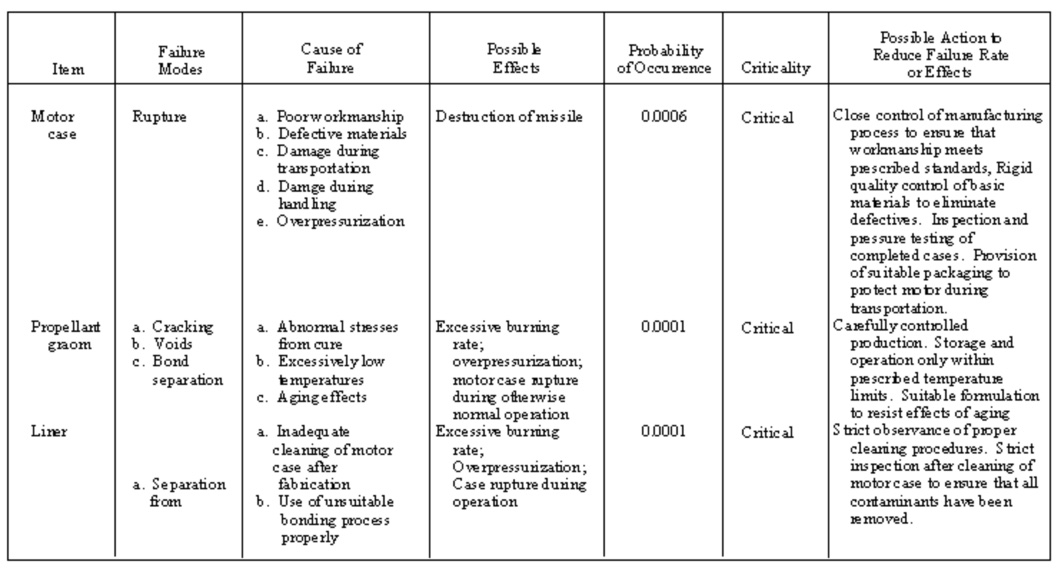
8.3. Failure Modes & Their Probability

A table like the one shown here from Greenberg and Cramer is used to identify a failure mode and its immediate consequences on the system. This enables the analyst to sort the results and produce a ranking of component failures. The ranking can be by system criticality or by probability of occurrence. This table shows the designation of a component failure by criticality and by probability of occurrence.
8.4. Required Documentation
This is a list of the documents required for an effective FMEA.
8.5. Other Documentation
Other information that would be used includes system descriptions, procedures and manuals as shown here.
8.6. Data Sheets
The overall objective is to organize and document the effect of component failures on the system. This information is captured in a data sheet. It includes the information shown on this slide. An example is shown on the next slide.
8.7. FMEA Data Sheet
Drawing Component Identifier Component and Failure Mode Method of Failure Detection Effect of System Other Remarks
HF-A-C A001AIRM line drainers wet air
HF-A-C A002AIRM plant air system drainers (2of2) wet air
HF-A-K A003AIRM Aftercooler trap A fails closed Compressor A fails
HF-A-G
HF-A-D
HF-A-F A004AIRM Aftercooler trap B fails closed Compressor B fails
HF-A-G
HF-A-D
HF-A-J A005AIRM Aftercooler trap C fails closed Compressor C fails
HF-A-G
HF-A-H A006AIRM Aftercooler trap D fails closed Compressor D fails
This is an example of an FMEA Data Sheet from Greenberg and Cramer. It shows the effect of the failure of cooling water flow on compressor failures. Although not shown on the sheet it identifies the failure of instrument power onto a pressure controller.
8.8. Advantages
There are several advantages associated with FMEA. It is easy to construct at the component level. Also, It is easy for the layperson to interpret. In addition, it requires less time than a more detailed study methodology. It quickly reveals fatal single failures when properly executed.
8.9. Disadvantages
However, there are also some disadvantages associated with FMEA. For instance, this analysis only addresses one component at a time. Therefore, it may not reveal important interactions between different components. Also, it fails to develop sufficient detail to provide a uniform basis for quantification of system effects. And last of all, it requires a great deal of experience from the study team to produce effective results. So FMEA, like a What–If analysis, is only as effective as the experience of the team members.